Recent successes and FDA approvals of CD19 redirected chimeric antigen receptor T cell (CART19) therapy have been achieved in pivotal clinical trials in patients with B cell malignancies. However, durable response rates in non-Hodgkin B cell lymphoma (B-NHL) and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) are low. Tumor-associated macrophages have emerged as key mediators of tumor-induced CART cell immunosuppression.
Axl receptor tyrosine kinase (Axl-RTK) is overexpressed in various human cancers including B-NHL or CLL and correlates with poor overall survival. Thus, several Axl-RTK inhibitors are currently being investigated in clinical trials. We have previously reported that the Axl-RTK inhibitor TP-0903 modulates CART19 function by Th1 polarization. Moreover, we observed a significant reduction in myeloid-derived cytokines in preclinical models. This led us to hypothesize that Axl-RTK inhibition also modulates monocytes which in turn affects CART function.
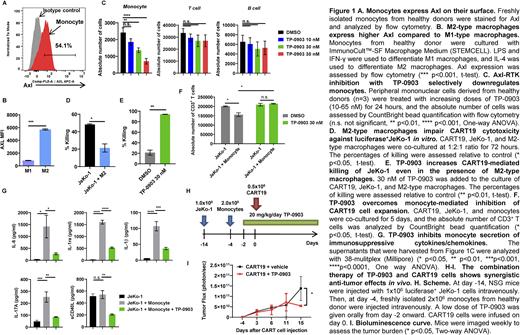
To test our hypothesis, we interrogated the interactions between Axl-RTK inhibition, monocytes, and CART. First, we isolated CD14+ monocytes from peripheral mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from healthy donors by magnetic negative selection. Flow cytometric analysis revealed a robust Axl expression on monocytes (Fig.1A). Monocytes were maintained in ImmunoCult Macrophage Medium (STEMCELL Technologies) and differentiated with lipopolysaccharide and interferon-γ for M1-type and interleukin (IL)-4 for M2-type macrophages. After confirming the macrophage phenotypes, cells were assessed for Axl expression. Flow cytometric analysis demonstrated that M2-type macrophages expressed higher Axl compared to M1 macrophages (Fig.1B).
Then, we treated PBMCs from healthy donors with TP-0903 for 24 hours to determine the specific cell types affected by Axl-RTK inhibition. Flow cytometric analysis revealed that monocytes were significantly inhibited by TP-0903 compared to B cells or T cells (Fig.1C). Having demonstrated that TP-0903 strongly suppresses monocytes and that M2-type macrophages express Axl on their surface, we then performed a cytotoxicity assay against CD19+ mantle cell lymphoma cell line, JeKo-1, to study the impact of Axl-RTK inhibition on monocyte-induced CART suppression. We used CART19 generated in our laboratory (FMC63-41BBζ). CART19, JeKo-1, and M2-type macrophages were co-cultured at 1:2:1 ratio and incubated for 3 days. The data revealed that M2-type macrophages strongly suppress CART19 killing (Fig.1D) which could be overcome with TP-0903 (Fig.1E). Next we studied monocyte-induced CART19 suppression with antigen-specific proliferation. CART19, JeKo-1, and monocytes were co-cultured at 1:5:1 ratio and incubated for 5 days. Flow cytometric analysis revealed that in the presence of monocytes, antigen-specific proliferation of CART19 was significantly suppressed, which was reversed in the presence of TP-0903 (Fig.1F). To assess how Axl inhibition modulates myeloid cell-derived cytokines/chemokines, we performed Multiplex (Millipore-Sigma) with the supernatants obtained from these co-culture assays. The presence of monocytes resulted in a significant increase in IL-17a, IL-6, IL-1 receptor agonist, IL-1β, and soluble CD40 ligand. However, Axl-RTK inhibition resulted in selective reduction of those cytokines/chemokines (Fig.1G) while preserving other effector cytokines.
Finally, we tested whether Axl-RTK inhibition with TP-0903 could overcome the negative effects of monocytes in vivo. Here, immunocompromised NSG mice were injected with 1x106 luciferase+ JeKo-1 cells intravenously. Ten days later, mice were injected with freshly isolated monocytes derived from a healthy donor. Two weeks after JeKo-1 inoculation, tumor burden was assessed with bioluminescence imaging. Mice were then randomized according to the tumor burden to receive 0.5x106 CART19 as a monotherapy or in combination with 20 mg/kg/day of oral TP-0903. The combination therapy resulted in superior anti-tumor effects and overall survival compared to CART19 monotherapy (Fig.1H-I).
In summary, Axl-RTK inhibition with TP-0903 demonstrates a direct suppression of inhibitory monocytes, which in turn enhances CART cell function. Our findings support the strategy of further refining and testing the novel and potent combination of Axl-RTK inhibition and CART cell therapy for the treatment of B cell malignancies.
Sakemura:Humanigen: Patents & Royalties. Cox:Humanigen: Patents & Royalties. Mouritsen:Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma Oncology, Inc.: Current Employment. Foulks:Tolero Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Current Employment. Warner:Tolero Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Current Employment. Ding:Merck: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; DTRM: Research Funding; Astra Zeneca: Research Funding; Abbvie: Research Funding; Octapharma: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; MEI Pharma: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; alexion: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Beigene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Parikh:GlaxoSmithKline: Honoraria; Verastem Oncology: Honoraria; Genentech: Honoraria; Ascentage Pharma: Research Funding; AbbVie: Honoraria, Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria, Research Funding; MorphoSys: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Honoraria, Research Funding. Kay:Pharmacyclics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; MEI Pharma: Research Funding; Abbvie: Research Funding; Tolero Pharmaceuticals: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Bristol Meyer Squib: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Acerta Pharma: Research Funding; Sunesis: Research Funding; Astra Zeneca: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Agios Pharma: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Cytomx: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Morpho-sys: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Rigel: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Oncotracker: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Dava Oncology: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Juno Theraputics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Kenderian:Mettaforge: Patents & Royalties; Lentigen: Research Funding; MorphoSys: Research Funding; Sunesis: Research Funding; Tolero: Research Funding; BMS: Research Funding; Juno: Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding; Kite: Research Funding; Novartis: Patents & Royalties, Research Funding; Torque: Consultancy; Humanigen: Consultancy, Patents & Royalties, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal